Tutorial: guidance for quantitative confocal microscopy
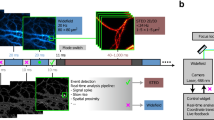
When used appropriately, a confocal fluorescence microscope is an excellent tool for making quantitative measurements in cells and tissues. The confocal microscope’s ability to block out-of-focus light and thereby perform optical sectioning through a specimen allows the researcher to quantify fluorescence with very high spatial precision. However, generating meaningful data using confocal microscopy requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of the technique. In this tutorial, the researcher is guided through all aspects of acquiring quantitative confocal microscopy images, including optimizing sample preparation for fixed and live cells, choosing the most suitable microscope for a given application and configuring the microscope parameters. Suggestions are offered for planning unbiased and rigorous confocal microscope experiments. Common pitfalls such as photobleaching and cross-talk are addressed, as well as several troubling instrumentation problems that may prevent the acquisition of quantitative data. Finally, guidelines for analyzing and presenting confocal images in a way that maintains the quantitative nature of the data are presented, and statistical analysis is discussed. A visual summary of this tutorial is available as a poster (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-0307-7).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
265,23 € per year
only 22,10 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Imagining the future of optical microscopy: everything, everywhere, all at once
Article Open access 28 October 2023
Practical considerations for quantitative light sheet fluorescence microscopy
Article 20 October 2022
Fast widefield scan provides tunable and uniform illumination optimizing super-resolution microscopy on large fields
Article Open access 24 May 2021
References
- Pawley, J. The 39 steps: a cautionary tale of quantitative 3-D fluorescence microscopy. Biotechniques28, 884–886 (2000). 888. ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- North, A. J. Seeing is believing? A beginners’ guide to practical pitfalls in image acquisition. J. Cell Biol.172, 9–18 (2006). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Hell, S., Reiner, G., Cremer, C. & Stelzer, E. H. K. Aberrations in confocal fluorescence microscopy induced by mismatches in refractive index. J. Microsc.169, 391–405 (1993). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Richardson, D. S. & Lichtman, J. W. Clarifying tissue clearing. Cell162, 246–257 (2015). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Allan, V. J. Basic immunofluorescence. in Protein Localization by Fluorescence Microscopy: A Practical Approach (ed. Allan, V. J.) 1–26 (Oxford University Press, 1999).
- McDonald, K. L., Morphew, M., Verkade, P. & Muller-Reichert, T. Recent advances in high-pressure freezing: equipment- and specimen-loading methods. Methods Mol. Biol.369, 143–173 (2007). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- North, A. J., Chidgey, M. A., Clarke, J. P., Bardsley, W. G. & Garrod, D. R. Distinct desmocollin isoforms occur in the same desmosomes and show reciprocally graded distributions in bovine nasal epidermis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA93, 7701–7705 (1996). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Burry, R. W. Immunocytochemistry: A Practical Guide for Biomedical Research (Springer, 2010).
- Park, Y. G. et al. Protection of tissue physicochemical properties using polyfunctional crosslinkers. Nat. Biotechnol.37, 73–83 (2019). ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Richter, K. N. et al. Glyoxal as an alternative fixative to formaldehyde in immunostaining and super-resolution microscopy. EMBO J.37, 139–159 (2018). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Melan, M. A. & Sluder, G. Redistribution and differential extraction of soluble proteins in permeabilized cultured cells. Implications for immunofluorescence microscopy. J. Cell Sci.101(Pt 4), 731–743 (1992). ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jamur, M. C. & Oliver, C. Permeabilization of cell membranes. Methods Mol. Biol.588, 63–66 (2010). ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yan, Q. & Bruchez, M. P. Advances in chemical labeling of proteins in living cells. Cell Tissue Res.360, 179–194 (2015). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Ries, J., Kaplan, C., Platonova, E., Eghlidi, H. & Ewers, H. A simple, versatile method for GFP-based super-resolution microscopy via nanobodies. Nat. Methods9, 582–584 (2012). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dolman, N. J., Kilgore, J. A. & Davidson, M. W. A review of reagents for fluorescence microscopy of cellular compartments and structures, part I: BacMam labeling and reagents for vesicular structures. Curr. Protoc. Cytom.65, 12.30.1–12.30.27 (2013). Google Scholar
- Kilgore, J. A., Dolman, N. J. & Davidson, M. W. A review of reagents for fluorescence microscopy of cellular compartments and structures, Part II: reagents for non-vesicular organelles. Curr. Protoc. Cytom.66, 12.31.1–12.31.24 (2013). Google Scholar
- Bordeaux, J. et al. Antibody validation. Biotechniques48, 197–209 (2010). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Pauly, D. & Hanack, K. How to avoid pitfalls in antibody use. F1000Res4, 691 (2015). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Stadler, C. et al. Systematic validation of antibody binding and protein subcellular localization using siRNA and confocal microscopy. J. Proteomics75, 2236–2251 (2012). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stack, R. F. et al. Quality assurance testing for modern optical imaging systems. Microsc. Microanal.17, 598–606 (2011). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cordes, T., Maiser, A., Steinhauer, C., Schermelleh, L. & Tinnefeld, P. Mechanisms and advancement of antifading agents for fluorescence microscopy and single-molecule spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.13, 6699–6709 (2011). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Piterburg, M., Panet, H. & Weiss, A. Photoconversion of DAPI following UV or violet excitation can cause DAPI to fluoresce with blue or cyan excitation. J. Microsc.246, 89–95 (2012). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Frigault, M. M., Lacoste, J., Swift, J. L. & Brown, C. M. Live-cell microscopy—tips and tools. J. Cell Sci.122, 753–767 (2009). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ettinger, A. & Wittmann, T. Fluorescence live cell imaging. Methods Cell Biol.123, 77–94 (2014). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Lambert, T. J. FPbase: a community-editable fluorescent protein database. Nat. Methods16, 277–278 (2019). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ai, H. W., Baird, M. A., Shen, Y., Davidson, M. W. & Campbell, R. E. Engineering and characterizing monomeric fluorescent proteins for live-cell imaging applications. Nat. Protoc.9, 910–928 (2014). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rodriguez, E. A. et al. The growing and glowing toolbox of fluorescent and photoactive proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci.42, 111–129 (2017). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cranfill, P. J. et al. Quantitative assessment of fluorescent proteins. Nat. Methods13, 557–562 (2016). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Bottanelli, F. et al. Two-colour live-cell nanoscale imaging of intracellular targets. Nat. Commun.7, 10778 (2016). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Erdmann, R. S. et al. Labeling strategies matter for super-resolution microscopy: a comparison between HaloTags and SNAP-tags. Cell Chem. Biol.26, 584–592.e6 (2019). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Wang, L. et al. A general strategy to develop cell permeable and fluorogenic probes for multicolour nanoscopy. Nat. Chem.12, 165–172 (2019). ArticlePubMedCASGoogle Scholar
- Grimm, J. B., Brown, T. A., English, B. P., Lionnet, T. & Lavis, L. D. Synthesis of Janelia Fluor HaloTag and SNAP-Tag ligands and their use in cellular imaging experiments. Methods Mol. Biol.1663, 179–188 (2017). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ferrando-May, E. et al. Advanced light microscopy core facilities: balancing service, science and career. Microsc. Res. Tech.79, 463–479 (2016). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Kiepas, A., Voorand, E., Mubaid, F., Siegel, P. M. & Brown, C. M. Optimizing live-cell fluorescence imaging conditions to minimize phototoxicity. J. Cell Sci.133, jcs242834 (2020). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Laissue, P. P., Alghamdi, R. A., Tomancak, P., Reynaud, E. G. & Shroff, H. Assessing phototoxicity in live fluorescence imaging. Nat. Methods14, 657 (2017). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jonkman, J. E., Swoger, J., Kress, H., Rohrbach, A. & Stelzer, E. H. Resolution in optical microscopy. Methods Enzymol.360, 416–446 (2003). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jacques, S. L. Optical properties of biological tissues: a review. Phys. Med. Biol.58, R37–R61 (2013). ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bolte, S. & Cordelieres, F. P. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc.224, 213–232 (2006). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dunn, K. W., Kamocka, M. M. & McDonald, J. H. A practical guide to evaluating colocalization in biological microscopy. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol.300, C723–C742 (2011). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Wallace, W., Schaefer, L. H. & Swedlow, J. R. A workingperson’s guide to deconvolution in light microscopy. Biotechniques31, 1076–1078 (2001). 1080, 1082 passim. ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jonkman, J. & Brown, C. M. Any way you slice it—a comparison of confocal microscopy techniques. J. Biomol. Tech.26, 54–65 (2015). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Korobchevskaya, K., Lagerholm, B. C., Colin-York, H. & Fritzsche, M. Exploring the potential of Airyscan microscopy for live cell imaging. Photonics4, 41 (2017). ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Zipfel, W. R., Williams, R. M. & Webb, W. W. Nonlinear magic: multiphoton microscopy in the biosciences. Nat. Biotechnol.21, 1369–1377 (2003). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Axelrod, D. Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy in cell biology. Traffic2, 764–774 (2001). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Power, R. M. & Huisken, J. A guide to light-sheet fluorescence microscopy for multiscale imaging. Nat. Methods14, 360–373 (2017). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Strobl, F., Schmitz, A. & Stelzer, E. H. K. Improving your four-dimensional image: traveling through a decade of light-sheet-based fluorescence microscopy research. Nat. Protoc.12, 1103–1109 (2017). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sigal, Y. M., Zhou, R. & Zhuang, X. Visualizing and discovering cellular structures with super-resolution microscopy. Science361, 880–887 (2018). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Wu, Y. & Shroff, H. Faster, sharper, and deeper: structured illumination microscopy for biological imaging. Nat. Methods15, 1011–1019 (2018). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ishikawa-Ankerhold, H. C., Ankerhold, R. & Drummen, G. P. Advanced fluorescence microscopy techniques—FRAP, FLIP, FLAP, FRET and FLIM. Molecules17, 4047–4132 (2012). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J. & Patterson, G. H. Development and use of fluorescent protein markers in living cells. Science300, 87–91 (2003). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J., Altan-Bonnet, N. & Patterson, G. H. Photobleaching and photoactivation: following protein dynamics in living cells. Nat. Cell Biol. Suppl, S7–S14 (2003).
- Elson, E. L. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: past, present, future. Biophys. J.101, 2855–2870 (2011). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Kim, S. A., Heinze, K. G. & Schwille, P. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy in living cells. Nat. Methods4, 963–973 (2007). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brown, C. M. et al. Raster image correlation spectroscopy (RICS) for measuring fast protein dynamics and concentrations with a commercial laser scanning confocal microscope. J. Microsc.229, 78–91 (2008). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Sprague, B. L. & McNally, J. G. FRAP analysis of binding: proper and fitting. Trends Cell Biol.15, 84–91 (2005). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Padilla-Parra, S. & Tramier, M. FRET microscopy in the living cell: different approaches, strengths and weaknesses. Bioessays34, 369–376 (2012). ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Broussard, J. A., Rappaz, B., Webb, D. J. & Brown, C. M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer microscopy as demonstrated by measuring the activation of the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Nat. Protoc.8, 265–281 (2013). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Bacia, K. & Schwille, P. Practical guidelines for dual-color fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy. Nat. Protoc.2, 2842–2856 (2007). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Krieger, J. W. et al. Imaging fluorescence (cross-) correlation spectroscopy in live cells and organisms. Nat. Protoc.10, 1948–1974 (2015). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Soderberg, O. et al. Direct observation of individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity ligation. Nat. Methods3, 995–1000 (2006). ArticlePubMedCASGoogle Scholar
- Holman, L., Head, M. L., Lanfear, R. & Jennions, M. D. Evidence of experimental bias in the life sciences: why we need blind data recording. PLoS Biol.13, e1002190 (2015). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralCASGoogle Scholar
- Kaptchuk, T. J. The double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial: gold standard or golden calf? J. Clin. Epidemiol.54, 541–549 (2001). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bankhead, P. et al. QuPath: open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep.7, 16878 (2017). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralCASGoogle Scholar
- Komura, D. & Ishikawa, S. Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J.16, 34–42 (2018). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Robertson, S., Azizpour, H., Smith, K. & Hartman, J. Digital image analysis in breast pathology—from image processing techniques to artificial intelligence. Transl. Res.194, 19–35 (2018). ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Howard, V. & Reed, M. G. Unbiased Stereology: Three-Dimensional Measurement in Microscopy (Springer, 1998).
- Kipanyula, M. J. & Sife, A. S. Global trends in application of stereology as a quantitative tool in biomedical research. Biomed. Res. Int.2018, 1825697 (2018). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Jonkman, J. E. et al. An introduction to the wound healing assay using live-cell microscopy. Cell Adh. Migr.8, 440–451 (2014). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Zimmermann, T., Marrison, J., Hogg, K. & O’Toole, P. Clearing up the signal: spectral imaging and linear unmixing in fluorescence microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol.1075, 129–148 (2014). ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jonkman, J., Brown, C. M. & Cole, R. W. Quantitative confocal microscopy: beyond a pretty picture. Methods Cell Biol.123, 113–134 (2014). ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oreopoulos, J., Berman, R. & Browne, M. Chapter 9—Spinning-disk confocal microscopy: present technology and future trends. in Methods in Cell Biology: Quantitative Imaging in Cell Biology Vol. 123 (eds Waters, J. C. & Wittman, T.) 153–175 (Academic Press, 2014).
- Model, M. A. & Blank, J. L. Concentrated dyes as a source of two-dimensional fluorescent field for characterization of a confocal microscope. J. Microsc.229, 12–16 (2008). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- International Organization for Standardization. Microscopes—Confocal microscopes—Optical data of fluorescence confocal microscopes for biological imaging. ISO Standard No. 21073:2019 (2019).
- Schindelin, J. et al. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods9, 676–682 (2012). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Arena, E. T. et al. Quantitating the cell: turning images into numbers with ImageJ. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol.6, e260 (2017). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Linkert, M. et al. Metadata matters: access to image data in the real world. J. Cell Biol.189, 777–782 (2010). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Arganda-Carreras, I. et al. Trainable Weka Segmentation: a machine learning tool for microscopy pixel classification. Bioinformatics33, 2424–2426 (2017). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tinevez, J. Y. et al. TrackMate: an open and extensible platform for single-particle tracking. Methods115, 80–90 (2017). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McQuin, C. et al. CellProfiler 3.0: next-generation image processing for biology. PLoS Biol.16, e2005970 (2018). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralCASGoogle Scholar
- Bray, M. A. et al. Cell Painting, a high-content image-based assay for morphological profiling using multiplexed fluorescent dyes. Nat. Protoc.11, 1757–1774 (2016). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Weigert, M. et al. Content-aware image restoration: pushing the limits of fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Methods15, 1090–1097 (2018). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Belthangady, C. & Royer, L. A. Applications, promises, and pitfalls of deep learning for fluorescence image reconstruction. Nat. Methods16, 1215–1225 (2019). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Royer, L. A. et al. ClearVolume: open-source live 3D visualization for light-sheet microscopy. Nat. Methods12, 480–481 (2015). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cromey, D. W. Avoiding twisted pixels: ethical guidelines for the appropriate use and manipulation of scientific digital images. Sci. Eng. Ethics16, 639–667 (2010). ArticlePubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Cromey, D. W. Digital images are data: and should be treated as such. Methods Mol. Biol.931, 1–27 (2013). CASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Goodwin, P. C. Quantitative deconvolution microscopy. Methods Cell Biol.123, 177–192 (2014). ArticlePubMedGoogle Scholar
- Allan, C. et al. OMERO: flexible, model-driven data management for experimental biology. Nat. Methods9, 245–253 (2012). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Ellenberg, J. et al. A call for public archives for biological image data. Nat. Methods15, 849–854 (2018). ArticleCASPubMedPubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
- Fay, D. S. & Gerow, K. A biologist’s guide to statistical thinking and analysis. WormBook Jul 9, 1–54 (2013).
- Vaux, D. L. Basic statistics in cell biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol.30, 23–37 (2014). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lacoste, J., Young, K. & Brown, C. M. Live-cell migration and adhesion turnover assays. Methods Mol. Biol.931, 61–84 (2013). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. Visualizing samples with box plots. Nat. Methods11, 119–120 (2014). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. Significance, P values and t-tests. Nat. Methods10, 1041–1042 (2013). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wasserstein, R. L., Schirm, A. L. & Lazar, N. A. Moving to a world beyond “p< 0.05”. Am. Stat.73, 1–19 (2019). ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Hibbs, A. R., MacDonald, G. & Garsha, K. Chapter 36: Practical confocal microscopy. in Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy 3rd edn (ed. Pawley, J. B.) (Springer, 2006).
- Wang, H., Lacoche, S., Huang, L., Xue, B. & Muthuswamy, S. K. Rotational motion during three-dimensional morphogenesis of mammary epithelial acini relates to laminin matrix assembly. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA110, 163–168 (2013). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
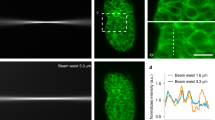
- Cole, R. W., Jinadasa, T. & Brown, C. M. Measuring and interpreting point spread functions to determine confocal microscope resolution and ensure quality control. Nat. Protoc.6, 1929–1941 (2011). ArticleCASPubMedGoogle Scholar
Acknowledgements
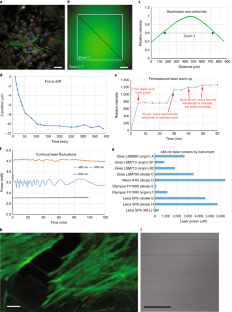
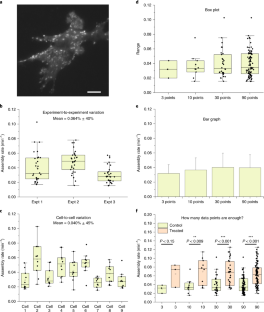
J.J. thanks the AOMF staff for helpful discussions, Courtney McIntosh for the images in Supplementary Fig. 1, and the Princess Margaret Foundation for ongoing financial support of the AOMF. G.D.W. thanks A*STAR and the National Research Foundation’s Shared Infrastructure Support Grant for continued support of the A*STAR Microscopy Platform and John Common for samples (Box 2). C.M.B. acknowledges Alex Kiepas (McGill University), who collected the adhesion dynamics data for the statistics section of the paper including Fig. 10, and the ABIF for general support and access to the Diskovery spinning disk TIRF microscope for collecting the adhesion dynamics data. K.I.A. thanks the Francis Crick Institute for their CALM support, and facility colleagues for helpful discussion. A.J.N. thanks the Rockefeller University for its continued support of the Frits and Rita Markus Bio-Imaging Resource Center (BIRC), the Sohn Conference Foundation for funding the Leica SP8 confocal microscope used to generate Figs. 3 and 4 and the facility staff and users for stimulating discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Advanced Optical Microscopy Facility (AOMF), University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada James Jonkman
- Advanced BioImaging Facility (ABIF), McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada Claire M. Brown
- A*STAR Microscopy Platform (AMP), Skin Research Institute of Singapore, A*STAR, Singapore, Singapore Graham D. Wright
- Crick Advanced Light Microscopy Facility (CALM), The Francis Crick Institute, London, UK Kurt I. Anderson
- Bio-Imaging Resource Center, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY, USA Alison J. North
- James Jonkman














